Depending on the location of the longhouse of a Mentawai family, fishing is conducted in any permanent water structure large enough to hold fish, gastropods, or crustaceans. In general, fishing is regarded as the work of men; women fish only with hand nets in terrestrial water bodies, or with scissor nets in the sea.
Fishing methods
Hand net fishing
Hand net fishing is often practiced in the island’s interior. It is typically done by women who wade up to their hips in slow-moving streams or channels. With a hand net, they try to catch freshwater prawns, crabs, frogs, and small fish. Additionally, they will collect larger specimens of freshwater snails. When wading, these women wear banana leaf aprons in deeper water, which the target animals see as a natural element. A thick section of bamboo pipe is inserted into the apron or strapped to their backs to collect the catch.
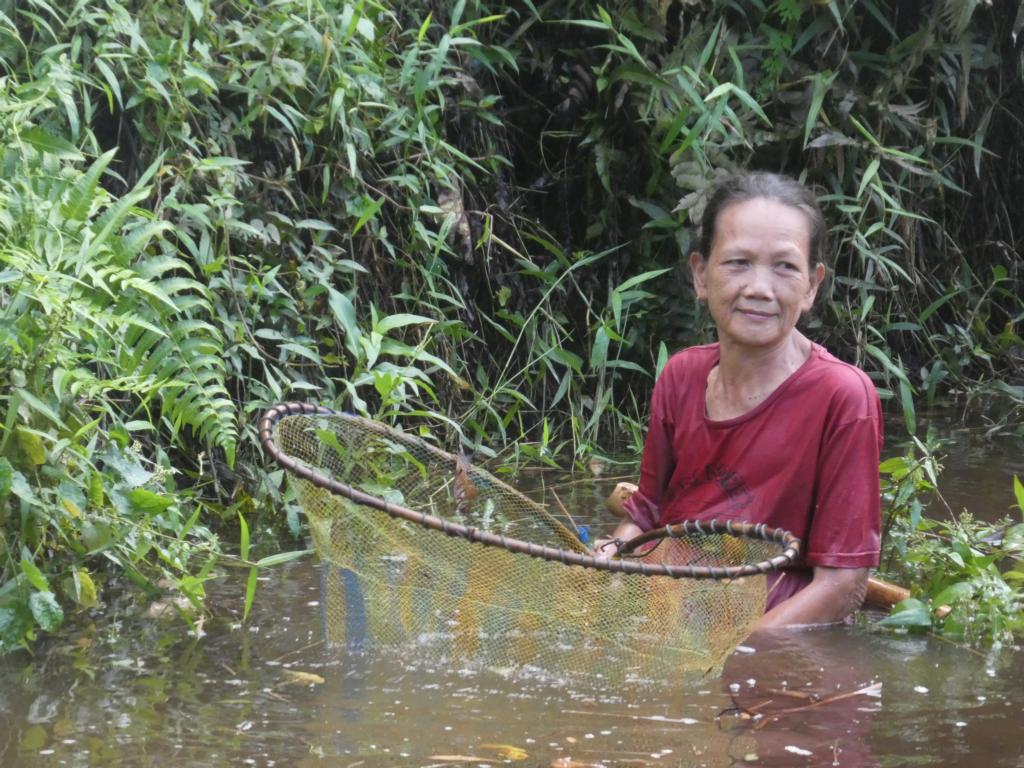

The fishing nets are largely imported. However, the Mentawai people also make them themselves. This is often a job for the women, who win the necessary yarn from the tree bark fibres of the Melinjo trees (Gnetum gnemon).
Spearfishing
Spearfishing was traditionally practiced in shallow and clear waters. The success rates increased at night when torches were used. However, nowadays, traditional spearfishing is no longer practiced.
On the other hand, a modern style of spearfishing with handheld spearguns is highly popular among the surfing community on the southern tip of Siberut Island. In general, places with sound waves for surfing are also good places for fishing, as a continental shelf drop-off close to the beach creates suitable surfing waves and brings large fish into close reach. Moreover, speargun fishing is a welcome distraction from the monotonous day-in, day-out activity of riding the waves.
Bow and arrow
According to Hansen (1915) , the Mentawai people use an arrow approximately 1.5 meters long to bow-shoot fish.
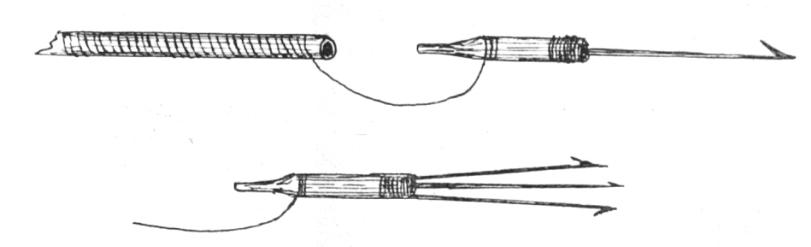
As arrowheads, they either use a harpoon-like tip or a trident-like arrowhead. Every arrow tip consists of a round piece of wood that either holds one or more barbed metal rods of iron, brass, or copper. This whole, tipped, round piece of wood is then stuck into the arrow shaft.

A long fishing line is wrapped around the arrow shaft, one end of which is tied to the tip and the other to the end of the shaft. If a fish is struck, the wounded animal shoots to the depths while struggling, with the point coming out of the handle. Then the fishing line unwinds from the handle, which, while floating, indicates the location. They then row to that place, seize the handle, and bring in the fish on the line.
Angling with hooks and hand lines.
No rods are used. This gear is either made from forest materials or purchased from village stores. For bait, insects or grubs are used. Hooks from forest materials are often not hooks in the ordinary sense, but small sticks with a sharp end on either side, with a line in the middle. These sticks will be stuck into the bait and taken by snakeheads or catfish. This way, these aggressive carnivorous fish will hook themselves as the stick in the bait turns in the stomach and holds the fish to the line. The catch rate of fish increases after heavy rain showers.
In former times, for angling, the lines were also made from the bark fibers of Melinjo trees. To improve their lifetime, they were treated with the juice of the Umbrella cheese tree (Glochidion sumatranum), which colored them a deep red.
Woven bamboo traps.
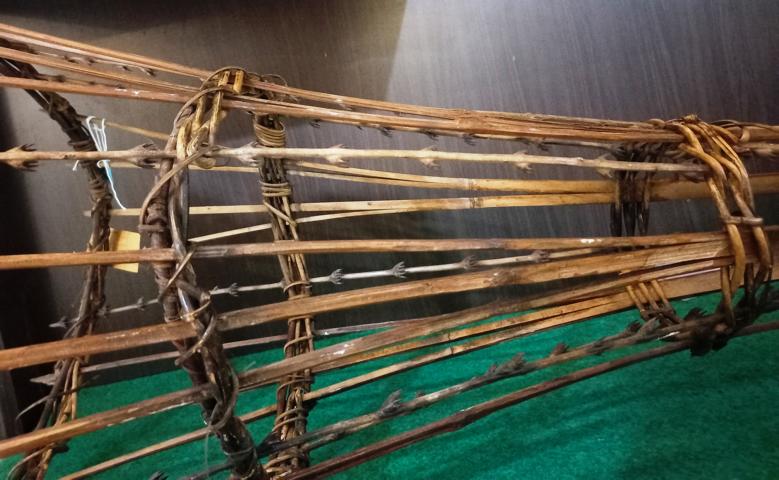

The Bahasa Indonesia (and Bahasa Malaysia) name for these traps is “bubu.” There is a wide variety of designs, all optimized for the behavior and size of the various fish species. For most of these traps, Pelege rattan vines are used for bindings, and Maggeak bamboo for the mesh sticks. For slender trap designs, rattan flagella are often woven into the trap to hold back fish that have entered. Nowadays, the use of bubus by Mentawai living in the forests is no longer common. Village Mentawai still use industrially manufactured Bubus of a rectangular design, covered with nylon mesh, in the Katurei Bay area.
Rotenone fishing.
This type of fishing is typically conducted during the dry season, when water levels are low. It involves stunning the fish, which return to life after a specified period. Mentawai crush the roots of Derris elliptica plants (Tuba), which they also use as an ingredient of the arrow poison. The roots of this plant contain rotenone, the most common fish poison worldwide.
After crushing these roots, the plant matter will be packed into the hiding places of small, secluded pools. The juice in the crushed roots colors the water milky-white, and fish coming in contact with it will be stupefied. After about 1 – 2 minutes, they will rise to the water surface and can be caught by hand. They can be eaten without any health issues.
Another method of rotenone fishing involves damming a section of a small river with a pool and placing a catching basket at the outlet. Then, on the inlet, men start crushing the Tuba roots, and the women catch the stunned fish. This is a type of social event that is only held occasionally.
Target fish species
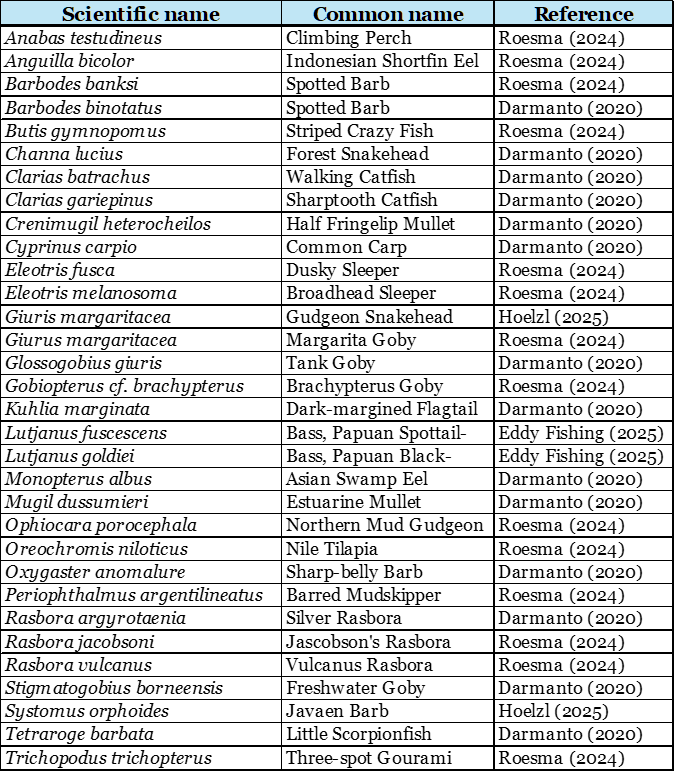
The Mentawai people primarily fish in the rivers, streams, brooks, channels, and swamps of Siberut Island, home to a diverse range of freshwater fish species. Combining the results of Roesma et.al (2024) and Darmanto (2020), Mentawai people eat a total of 32 freshwater species on Siberut Island.
Anabantiformes
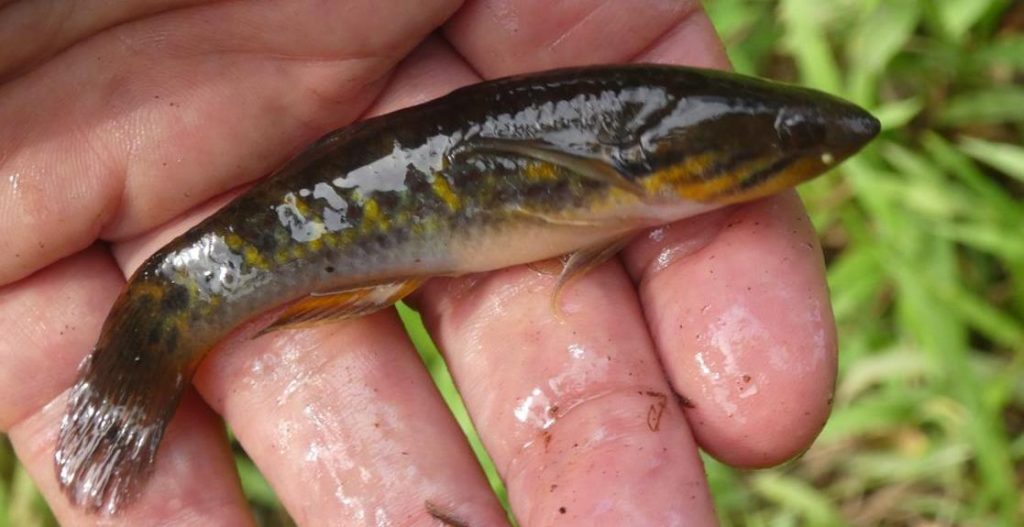

The first order of caught fish is labyrinth fish (Anabantiformes). The best-known taxonomic family within this order is Snakeheads (Channidae). They are represented at Siberut by the Forest Snakehead and Gudgeon Snakehead species.

Another species within the Anabantiformes order is the Climbing Perch. These small fish can breathe air, survive out of water for 6 to 8 hours, and can walk on land. They prefer shallow, stagnant, and muddy waters. They are mainly caught by hand netting or bamboo traps. Standard preparation methods are roasting and smoking.
Eels
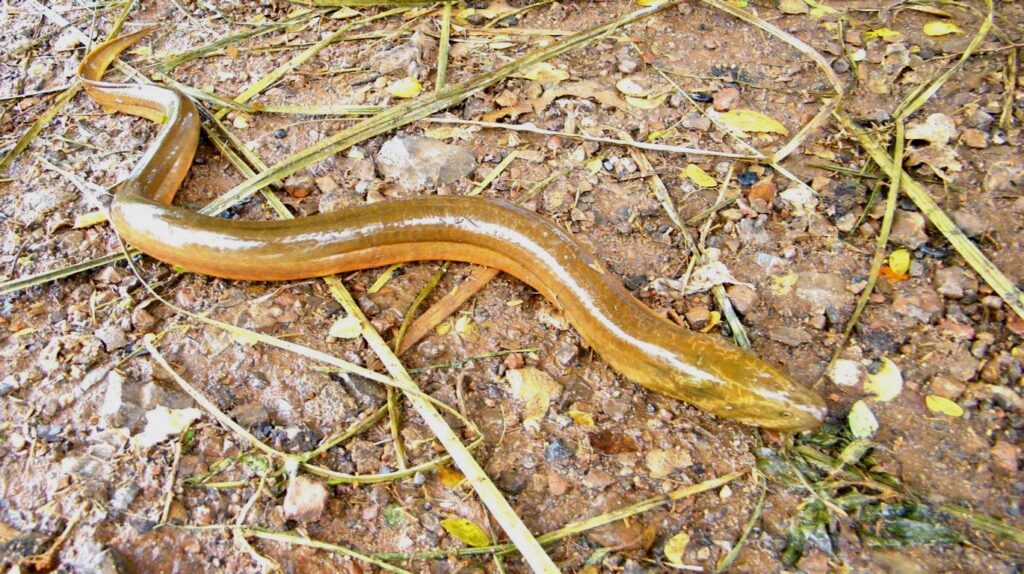

The Shortfin Eel (Anguilla bicolor) is found under rocks and on river banks and is caught with hand nets or bamboo traps. Asian swamp eels (Monopterus albus), locally called Sikapla, are caught with hooks and line or with basket traps. Both eel species are easier to catch after rain, when the water is murky. When fishing with a hook and line, the favorite bait for eels is sago grubs.
Cyprinoformes
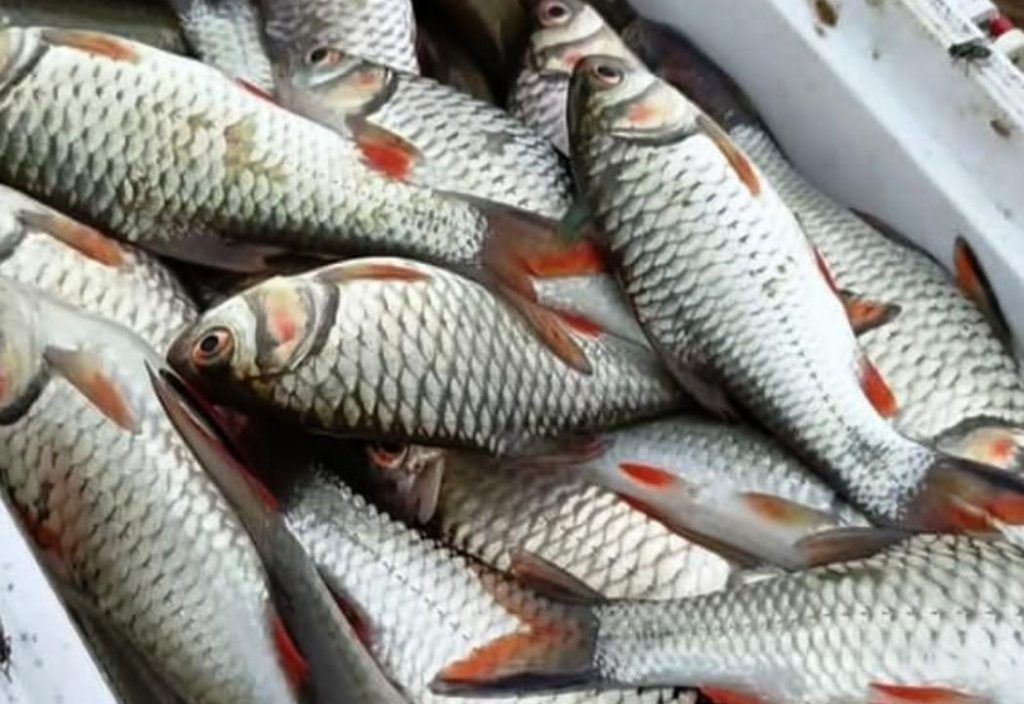

The order of Cypriniformes is represented by the Spotted Barb and two Rasbora species. They are small to medium-sized fish, ranging from 1 to 8 inches (2.5 to 20 cm) in length, that prefer clear and clean water. Hand nets, bamboo traps, and rotenone are used to catch them. The larger sizes are grilled, and the smaller ones are cooked in soups.
Gobiiformes
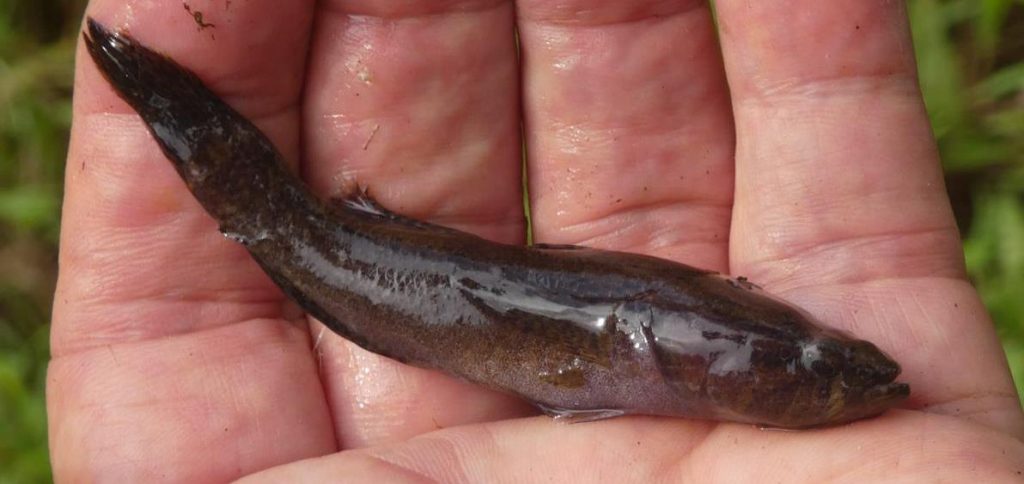

Most fish caught are of the order Gobiiformes. These Gobi-like fish are bottom-dwelling species common in all running freshwater habitats. Due to their small size, they are either caught by hand nets or bamboo traps. The Mentawai call the Goby fish species ‘Jumbo’.
Cichlidae
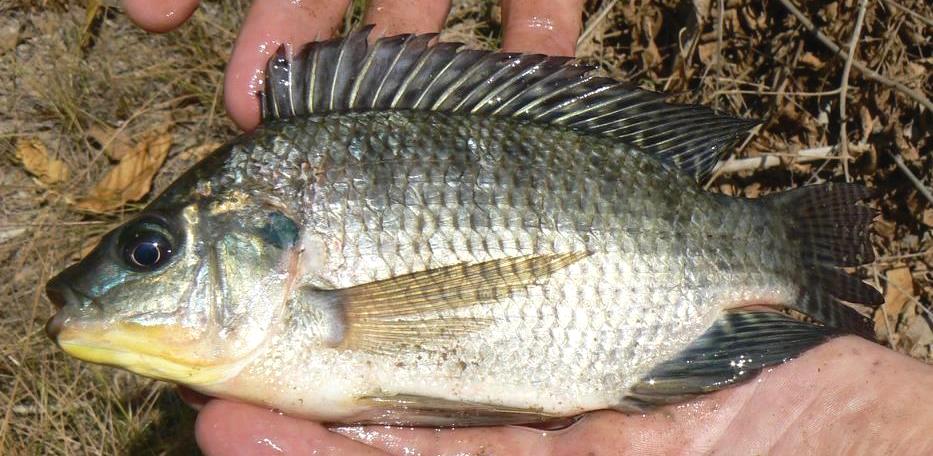

The Nile Tilapia is the only representative of the Cichlidae family. It is not an endemic fish species; it was introduced and has become an invasive species. It grows quickly, is easily caught using various methods, and has a good taste. However, it likes to feed on the eggs of endemic fish species.
Siluriformes
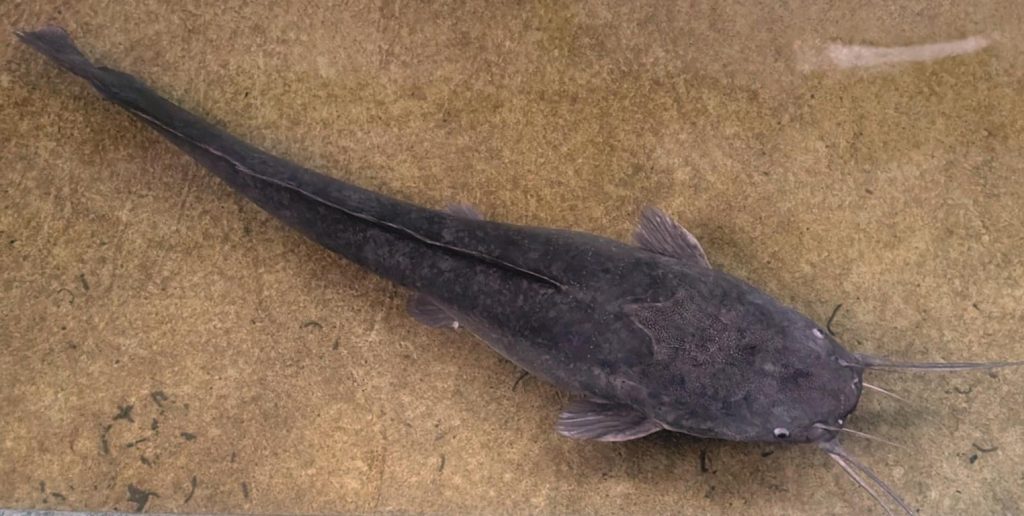

Furthermore, the Siluriformes are represented on Siberut Island by two species, the Walking Catfish (Tuik)and the Sharptooth Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). They are found in streams and rivers, especially in the rainy season, and also in murky backwaters. These fish are primarily caught by angling or in bamboo traps. They are popular for grilling or smoking, but their meat always has a touch of muddiness.
Freshwater Snapper
Besides all these discussed fish species, sports anglers like to come to the Mentawai islands for catching Papuan Spottail Bass (Lutjanus fuscescens), also called ‘Freshwater snapper’, and Papuan Black Bass (Lutjanus goldiei). Both species occur in large freshwater streams and in brackish mangrove areas. Due to their large size, they are not a typical target for the forest-dwelling Mentawais and are seldom caught by them.
Lessons learned about freshwater fishing at Siberut Island:
- Hand net fishing is the most popular method of catching small fish and crustaceans.
- Climbing perch, shortfin eel, gobi-like fish, and walking catfish are caught in muddy waters.
- Spotted barbs and rasboras are fish of the clear streams and brooks.
.





